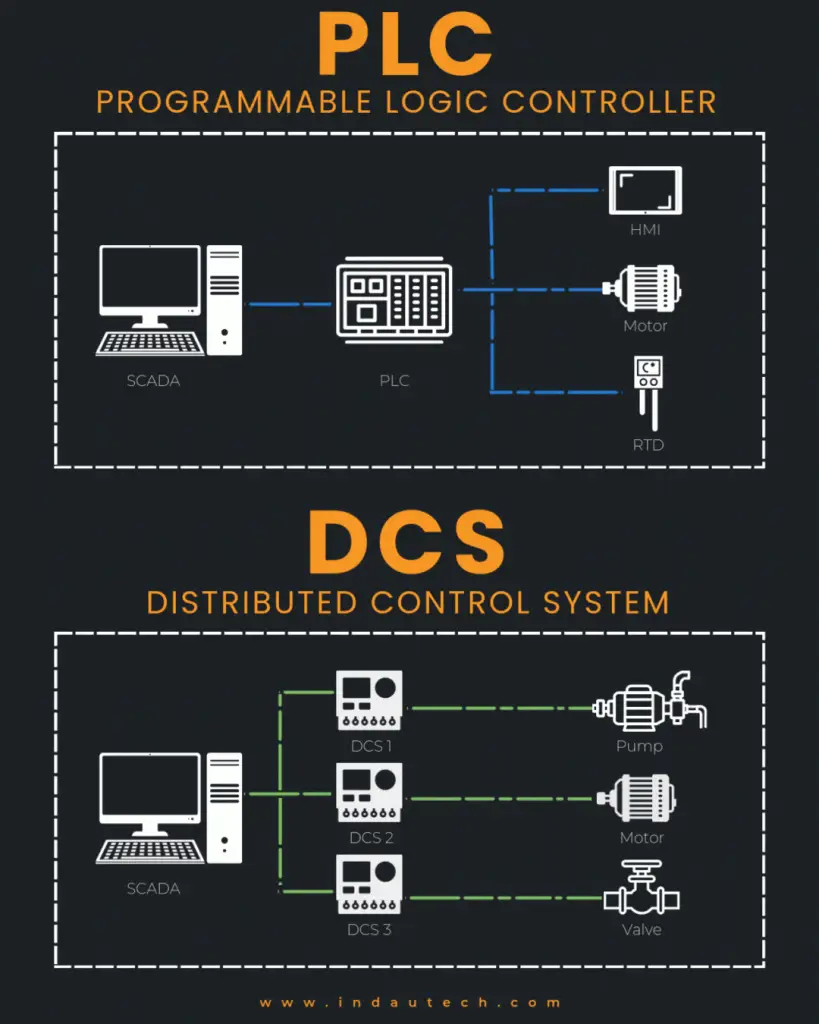
PLC ( Programmable Logic Controller) :
A ruggedized digital computer designed for automation tasks in manufacturing and industrial processes. It excels in fast, sequential control and is commonly used for specific, medium-scale applications.
DCS (Distributed Control System) :
A system designed for large, complex industrial processes like chemical plants or power plants. It emphasizes process control and integrates multiple subsystems across a plant.
Differences:
- Control Scope: PLCs are better in discrete and fast control tasks, while DCS are more capable of handling complex and large-scale process automation.
- Architecture: PLCs are standalone or networked controllers, DCS relies on a centralized, hierarchical system.
- Scalability: PLCs are more affordable for smaller systems while DCS are usually used for large, integrated processes.
- Programming: PLCs use ladder logic , Structured Texts or function blocks , DCS uses function blocks with advanced graphical interfaces.
- Applications: PLCs are ideal for machinery control and factory automation, while DCS dominates in process industries like oil, gas, and chemicals.